Understanding The Difference Between Chromatin And Chromatid
Chromatin and chromatid are two essential components of cellular biology, playing crucial roles in DNA organization and cell division. While they are related, they serve distinct functions within the cell, and understanding their differences is vital for grasping how genetic information is stored, replicated, and transmitted. Chromatin refers to the complex of DNA and proteins that make up chromosomes, while chromatids are the replicated copies of chromosomes that appear during cell division. This article dives deep into the topic of chromatin vs chromatid, breaking down their roles, structures, and importance in cellular processes.
For students, researchers, and biology enthusiasts, distinguishing between chromatin and chromatid can sometimes be confusing due to their interconnected nature. Chromatin is the relaxed, uncoiled form of DNA that allows for gene expression and replication, while chromatids are the tightly coiled structures that ensure accurate chromosome segregation during mitosis and meiosis. Understanding these differences is not only fundamental for academic purposes but also for advancing scientific research in genetics and molecular biology.
In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the definitions, functions, and structural differences of chromatin and chromatid. By the end of this article, you will have a clear understanding of how these components contribute to cellular processes and why they are critical for life. Whether you're preparing for an exam or simply curious about the intricacies of biology, this article is designed to provide valuable insights into the fascinating world of chromatin vs chromatid.
Read also:Cyber Sigilism The Intersection Of Technology And Mysticism
- What is Chromatin?
- What is a Chromatid?
- How Are Chromatin and Chromatid Different?
- Why is Chromatin Important in Cell Biology?
- What Role Do Chromatids Play in Cell Division?
- How Does Chromatin Become Chromatid?
- Common Misconceptions About Chromatin vs Chromatid
- Frequently Asked Questions About Chromatin and Chromatid
- The Importance of Studying Chromatin and Chromatid
- Conclusion
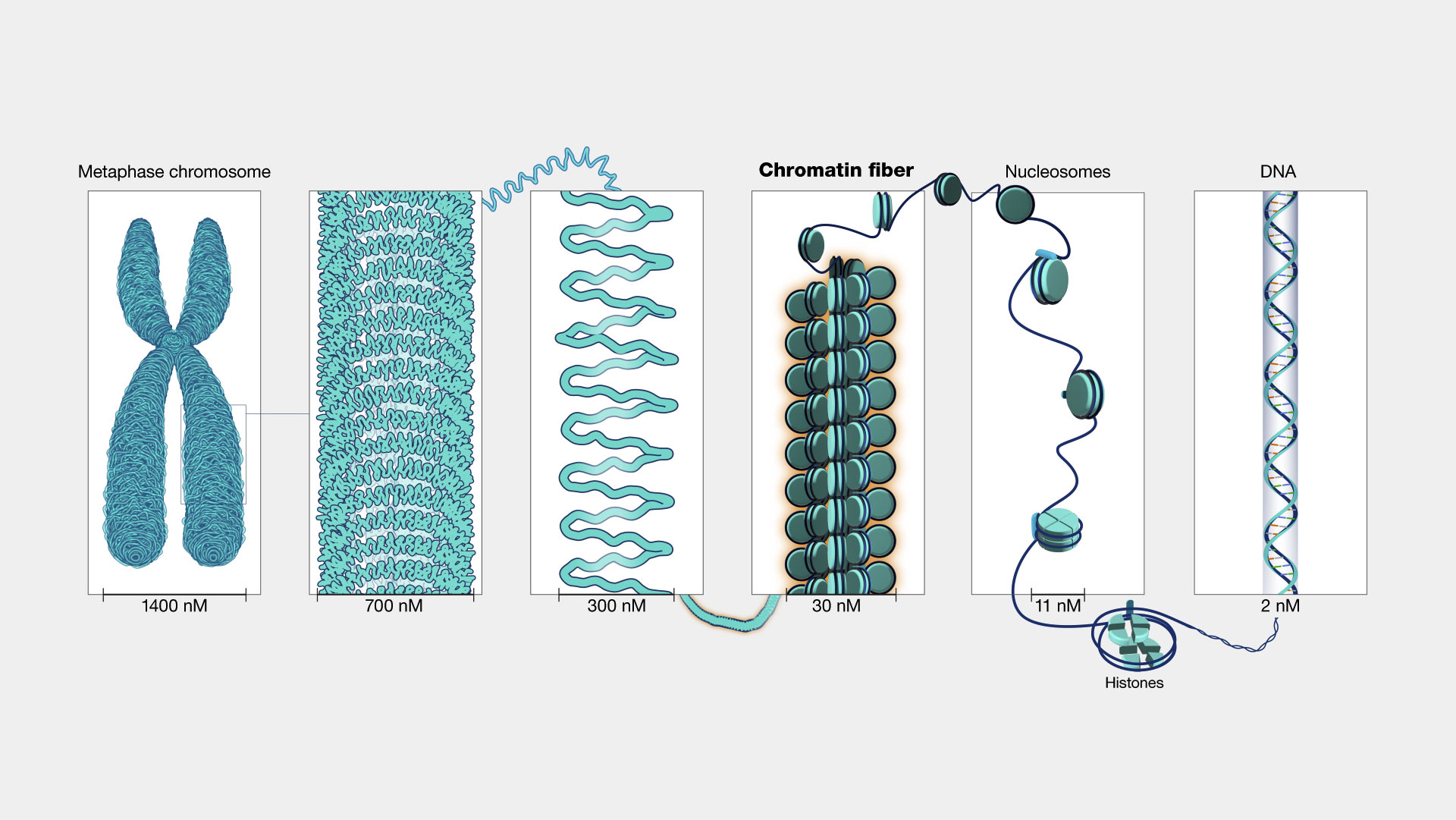
What is Chromatin?
Chromatin is a complex of DNA, RNA, and proteins that forms the structural foundation of chromosomes in eukaryotic cells. It exists in two forms: euchromatin, which is loosely packed and transcriptionally active, and heterochromatin, which is tightly packed and transcriptionally inactive. The primary function of chromatin is to package long strands of DNA into a compact structure that fits within the nucleus of a cell.
- Chromatin allows for efficient DNA replication and transcription.
- It plays a critical role in regulating gene expression.
- Chromatin remodeling is essential for cellular processes like repair and recombination.
Without chromatin, the DNA molecule, which is approximately 2 meters long in humans, would be unable to fit inside the microscopic nucleus. This highlights the importance of chromatin in maintaining cellular integrity and function.
What is a Chromatid?
A chromatid is one of two identical copies of a replicated chromosome, joined together at the centromere. Chromatids are formed during the S phase of the cell cycle when DNA is duplicated. During mitosis or meiosis, chromatids are pulled apart to ensure that each daughter cell receives an identical set of chromosomes.
Chromatids are temporary structures that only exist during cell division. They are essential for ensuring genetic stability and preventing errors such as aneuploidy, which can lead to developmental disorders or cancer. Understanding the role of chromatids is crucial for comprehending the mechanisms of heredity and genetic diversity.
How Are Chromatin and Chromatid Different?
While chromatin and chromatid are both involved in DNA organization, they differ significantly in structure, function, and timing within the cell cycle. Here’s a detailed comparison:
| Aspect | Chromatin | Chromatid |
|---|---|---|
| Structure | Loosely packed DNA-protein complex | Tightly coiled, duplicated chromosome |
| Function | Gene expression and DNA replication | Ensures equal chromosome distribution during cell division |
| Timing | Present throughout the cell cycle | Forms during the S phase and exists during mitosis/meiosis |
Why is Chromatin Important in Cell Biology?
Chromatin is vital for maintaining genomic stability and regulating gene expression. Its dynamic structure allows cells to control which genes are active or inactive at any given time. This regulation is crucial for processes such as development, differentiation, and response to environmental stimuli.
Read also:Telugu Sex Photos Understanding The Cultural And Social Implications
What Role Do Chromatids Play in Cell Division?
Chromatids ensure that genetic material is accurately distributed to daughter cells during mitosis and meiosis. Errors in chromatid separation can lead to chromosomal abnormalities, which may result in diseases such as Down syndrome or cancer.
How Does Chromatin Become Chromatid?
During the S phase of the cell cycle, chromatin undergoes a series of changes to form chromatids. DNA replication produces two identical DNA molecules, which are then tightly coiled and condensed to form sister chromatids. This transformation is essential for the proper segregation of chromosomes during cell division.
Common Misconceptions About Chromatin vs Chromatid
One common misconception is that chromatin and chromatid are interchangeable terms. However, they refer to different stages and forms of DNA organization. Chromatin is present throughout the cell cycle, while chromatids only exist during specific phases of cell division.
Frequently Asked Questions About Chromatin and Chromatid
Here are some frequently asked questions about chromatin and chromatid:
- What is the main difference between chromatin and chromatid?
- When do chromatids form during the cell cycle?
- How does chromatin regulate gene expression?
- Can errors in chromatid separation cause diseases?
The Importance of Studying Chromatin and Chromatid
Studying chromatin and chromatid is essential for advancing our understanding of genetics, molecular biology, and medicine. Research in this field has led to breakthroughs in cancer therapy, developmental biology, and genetic engineering.
Conclusion
Chromatin and chromatid are fundamental components of cellular biology, each with unique roles and characteristics. By understanding the differences between chromatin vs chromatid, we gain valuable insights into the mechanisms of DNA organization, replication, and inheritance. This knowledge not only enhances our academic understanding but also paves the way for advancements in science and medicine.
Tyron Woodley TV Shows: A Deep Dive Into His Acting Journey
Methstrems: Unlocking The Power Of Streamlined Solutions
Haleyybaylee Age: Unveiling The Story Behind The Rising Star
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/homologous-chromosomes-with-annotations--764793193-5c43e02fc9e77c00018e6540.jpg)
Chromatid Biology Simple
Chromatin